X - Rays and Bragg's Law
X - Rays and Bragg's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Applications of X-rays, X-ray, Production of X-rays in Coolidge Tube, Discharge Tube, Cathode Rays, Soft X-rays, Hard X-rays & Properties of X-rays etc.
Important Questions on X - Rays and Bragg's Law
How are the diodes used in rectification process?
Why high voltage is used in discharge tube?
What is the application of discharge tube?
Which of the following results is correct, if the potential difference between the anode and cathode of the -ray tube increases ?
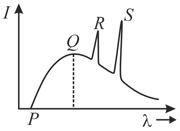
The voltage applied to the Coolidge -ray tube is increased by . As a result, the short wave limit of continuous -ray spectrum shifts by . The initial voltage applied to the tube is
The potential difference applied to an X - ray tube is 5 kV and the current through it is 3.2 mA. The number of electrons striking the target per second is .............. (Take )
If the potential difference applied across -ray tube is volts, then approximately minimum wavelength of the emitted -rays will be
Energy of characteristic -ray is a consequence of
The filament current in the electron gun of a coolidge tube is increased while the potential difference used to accelerate the electrons is decreased. As a result, in the emitted radiation
A potential difference of is applied across an X - rays tube. The ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength of the incident electrons to the shortest wavelength of X - rays produced is ( C/kg for an electron)
-rays of wavelength are scattered from a block of material The scattered -rays are observed at an angle of to the incident beam. Calculate their wavelength.
X-rays are produced in an X-ray tube operating at a given accelerating voltage. The wavelength of the continuous X-rays has values from
The X-ray beam coming from an X-ray tube will be
